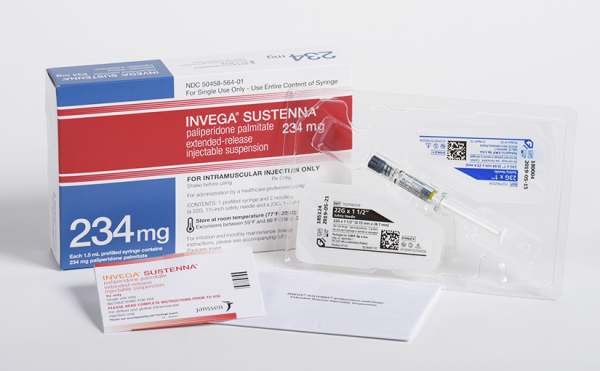
Whilst herpes zoster or shingles are rarely life-threatening, you should exercise caution and seek prevention as soon as possible. Being a solution to decrease the risk of disease, Zostavax after the shingles outbreak is a vaccine that has a higher potency to boost people’s immune response against the virus.
However, it is important to pay attention that not everyone can receive Zostavax, as well as the other adverse effects of the vaccine. To get a detailed explanation, dig deeper into the following explanation!
The Overview of Zostavax After Shingles Outbreak
According to Medsafe, Zostavax is a live and attenuated varicella-zoster virus (VZV) vaccine that contains 14 times the virus found in childhood varicella vaccines.
Meanwhile, the Food and Drug Administration reports that inactive ingredients include sucrose, hydrolyzed porcine gelatin, sodium chloride, monosodium, L-glutamate, sodium phosphate dibasic, potassium phosphate monobasic, potassium chloride, and urea.
Generally, Zostavax is indicated for preventing herpes zoster or shingles outbreaks in patients aged 50 years and older.
Shingles or herpes zoster, can occur in people of all ages and the risk increases as people get older. It is caused by the same virus (varicella) that leads to chickenpox in children. When the virus reactivates in an adult, it can lead to herpes zoster or shingles.
Zostavax works by exposing to a small amount of live virus, then boosting the body to develop immunity against the disease. This vaccine will not treat an existing infection in the body.
However, the administration of Zostavax is contraindicated and can result in illness from the vaccine virus in individuals who are immunosuppressed or immunodeficient from either primary or acquired medical conditions.
This type of vaccine is not only for preventing shingles outbreaks but also for treating postherpetic neuralgia and zoster-related chronic pain in people 60 years of age and over. For information, children are not allowed to take this vaccine as medicine, since it will harm this population.
The Precaution Before Using Zostafax After Shingles Outbreak
This vaccine is typically not recommended for people with weakened immune systems, but it is more than that. Don’t be careless; there are several precautions you should take actions before using this type of Zoster vaccine. Several numbers listed below serve as a guide for understanding the vaccine prohibitions.
1. Pregnant and Breast Feeding Women
First rule, pregnant women should not receive Zostavax. According to the My Surgery website, women with childbearing potential should follow the necessary precautions to avoid pregnancy for one month after vaccination.
You should clearly inform your physician if you are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Your doctor will decide whether Zostavax should be administered or not. Furthermore, if you are planning to have a baby ask the doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking the vaccine.
2. TBC, Leukemia, Lymphoma, or Other Cancer Affecting Bone Marrow
You can still get vaccinated if you have a minor cold. However, patients with tuberculosis (TBC) or any other severe illness with a fever or infection should wait until they feel better before receiving Zostavax.
Further, since the Zostavax after shingles outbreak includes a live virus, it should not be given to people with leukemia, lymphoma, or any other cancer that affects bone marrow. In addition, patients who undergo chemo or radiotherapy are also prohibited from using the vaccine as the protection
3. People With Allergic Reactions to Neomycin or Gelatin
The third rule is that people with a history of allergic reactions to neomycin (Neo-Tab, Neo-Fradin, Mycifradin) or even gelatin should not be given the Zostavax vaccine. The symptoms of an allergic version may cause difficulty in breathing and swelling on the body’s part, such as the face, lips, tongue as well as throat.
How Does the Zostavax After Shingles Outbreak Given?
First of all, you will get this vaccine in a doctor’s office or another clinic setting. Zostavax is typically given a single 0.65 mL dose by an injection under the skin, preferably in the upper arm.
Here, health professionals should consider a patient’s immunological status before vaccination and do not administer Zostavax in immunosuppressed patients. If unsure, postpone vaccination and seek professional advice.
You also should not receive the Zostavax after shingles outbreak if you have previously had a serious allergic reaction to a previous dose of the zoster. This prohibition also applies to those who had an allergic reaction to any of the vaccine’s ingredients, even a previous dose of the varicella injection.
If you have a blood clotting disorder or blood’s low platelet levels, the injection will be administered beneath the skin.
Another thing you must remember is to read the patient information, medication guides, and instruction sheets provided to you. Zostavax is administered as a time injection, so you are unlikely to follow a dosing schedule unless the doctor instructs you otherwise.
Do not hesitate to talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you have any urgent questions right away.
What is The Side Effect of Zostavax After Shingles Outbreak?
Similar to vaccines and medicines in common, Zostavax can cause side effects, even though not everybody experiences them. Allergic reactions can occur very rarely (up to one in every 1,000 people).
Some of these reactions may be serious, causing tough swallowing or even breathing. Nonetheless, the risks of serious side effects are extremely low.
For more details, the following symptoms are another adverse effect of this type of Zostavax after a shingles outbreak. It has been observed in clinical trials and through post-marketing surveillance.
1. Very common: Redness, pain, swelling, and itching at the injection side.
2. Common: Warmth, fever, headache, bruising, hard lump, injection site rash, pain in the arm or leg, joint pain, muscle pain.
3. Uncommon: Nausea, swollen gland.
4. Rare: Injection site hive.
5. Very rare: Chickenpox (varicella) and shingles.
Getting infected with shingles is far more harmful to your health than getting the vaccine to prevent it. Still, observe any side effects you experience after receiving the vaccine. If you need a booster dose, tell your doctor that the previous injection caused any side effects.
Is Zostavax After Shingles Outbreak Beneficial For Health?
In conclusion, Zostavax is safe and generally well-tolerated among people with age 50 years old and older. Overall, the vaccine has a positive effect on reducing the risk of developing herpes zoster or shingles outbreaks.
Despite being widely used in the United States, unfortunately, the Zostavax vaccine was discontinued in July 2020. After only a few years, it became clear that it was not as effective as previously thought.
For certain patients, the shingles virus strain in Zostavax was not sufficiently diluted, resulting in a variant strain of the shingles virus.
Bagikan